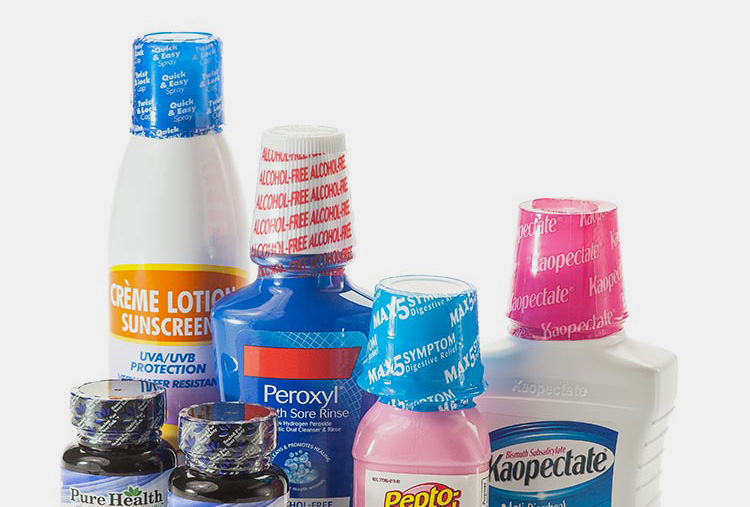
Heat Shrink Tunnel:The complete FAQ Guide in 2024
Heat Shrink Tunnel:The complete FAQ Guide in 2024
Are you familiar with a heat shrink tunnel? Do you know how a heat shrink tunnel can be of benefit to your business? You are at the right place! A heat shrink tunnel is a type of machinery used to shrink wrappers around products. The resulting film is tight and secure, providing a protective layer for whatever it is that you have wrapped.
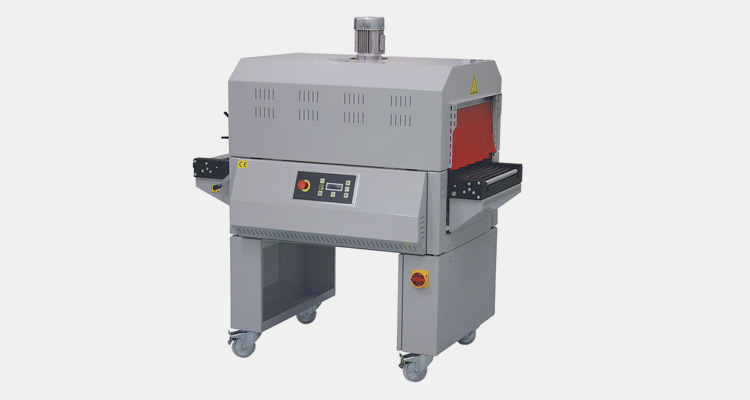

Heat shrink tunnels come in all shapes and sizes, so it is important to do your research before purchasing one. Therefore, if you are considering purchasing a heat shrink tunnel, this blog will add up to your information. Now, let’s get to learn more about this amazing equipment.
1.What Is A Heat Shrink Tunnel?
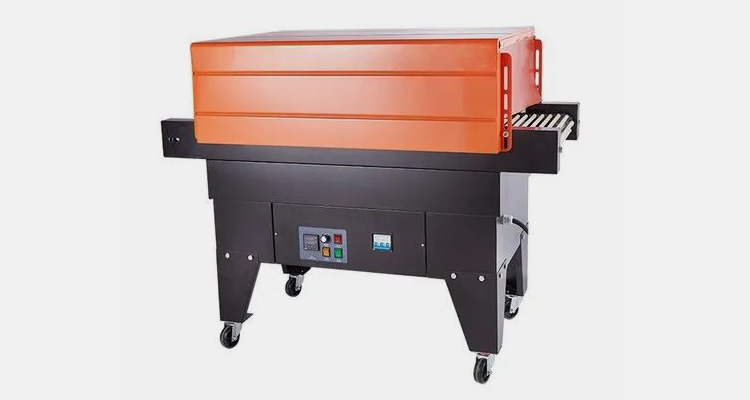

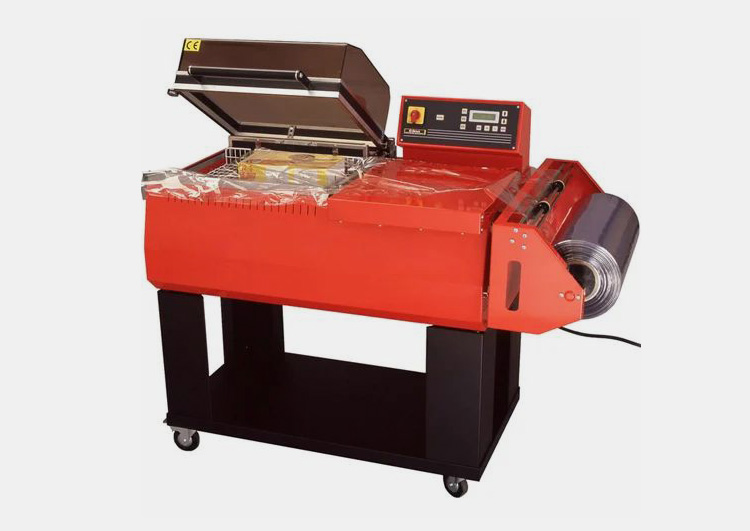
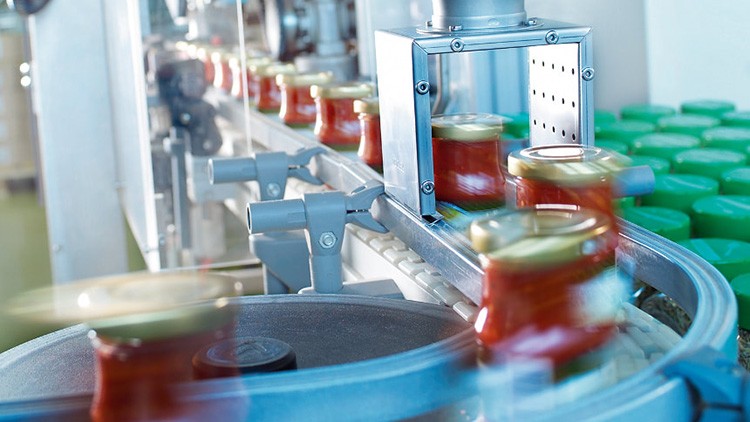
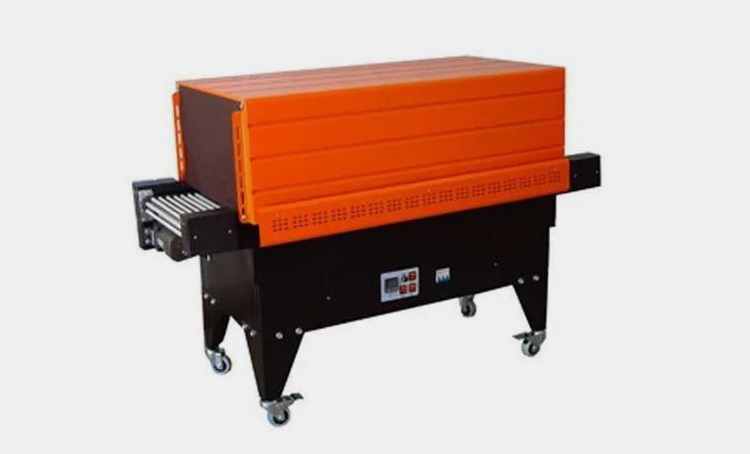
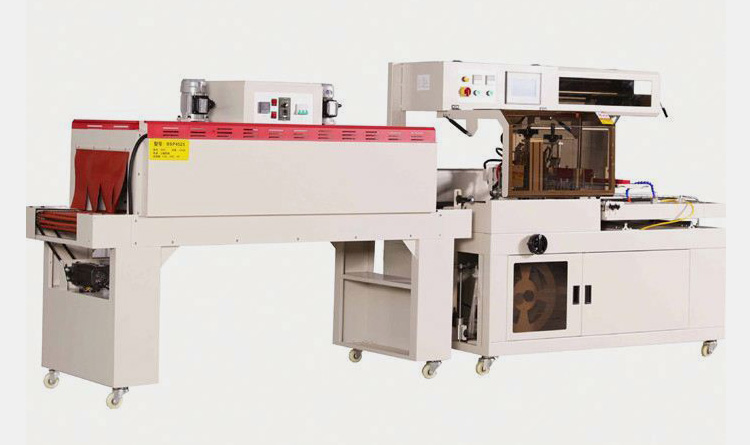
A Heat Shrink Tunnel is a machine that uses hot air to reduce the size of shrink film and create a tight, uniform fit around products. Heat shrink tunnels are typically used in packaging for food, beverages, cosmetics and other consumer goods. Usually, heat is applied from all sides through an enclosed chamber which shrinks the film around the product to create a tight and secure seal.
Heat shrink tunnels are used in the electronics industry for shrinking wire harnesses, connectors and other components. Also, these devices offer cost-effective solutions for quickly and easily packaging products for safe storage and transport. Additionally, they help protect goods from dust and moisture during transit, thus making them ideal for shipping applications.
Moreover, these machines are a great way to improve the efficiency and productivity of your packaging line. Their ability to quickly and uniformly shrink film around products can help reduce errors and save time in the long run. Ultimately, this equipment offers an efficient solution for sealing product packages with minimal effort.
2.How Does A Heat Shrink Tunnel Work?
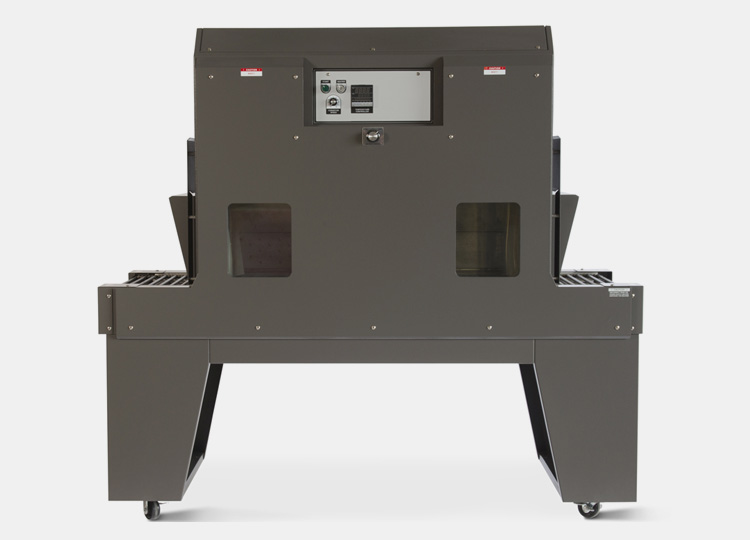

Heat shrink tunnel works by circulating heated air through the tunnel chamber, which then passes over the heat-shrinkable material. This heat helps the fabric to contract and shape itself around the product, creating a tight fit to protect it from damage or dust.
This equipment consists of a chamber with an opening at each end, through which the material to be shrunk is fed. Inside the chamber, a series of heat lamps or radiant heaters evenly heats the material as it moves through the tunnel on a conveyor belt.
As the material is heated, it begins to shrink in size. The shrinkage depends on the type of material and the temperature at which it is heated. Once the desired shrinkage has been achieved, the material is cooled and discharged from the heat shrink tunnel.
3.What Are The Components Of A Heat Shrink Tunnel?
A heat shrink tunnel is composed of different constituents that work together to heat and shrink heat-shrinkable films for packaging applications. These components include:
Conveyor Belt
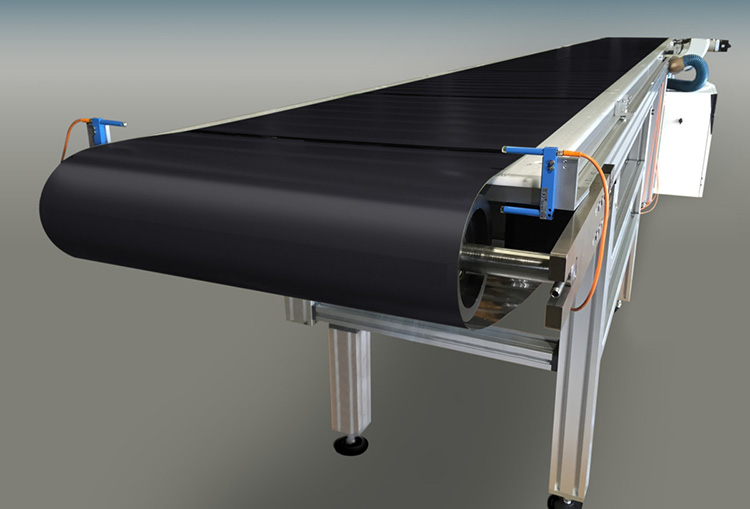
A conveyor belt transports the items through heat-shrinking while the heat source heats them. Modern heat shrink tunnels may have adjustable speed conveyors that run at different speeds depending on how large or small packages need to be shrunk and how quickly they need to be processed.
Heat Source
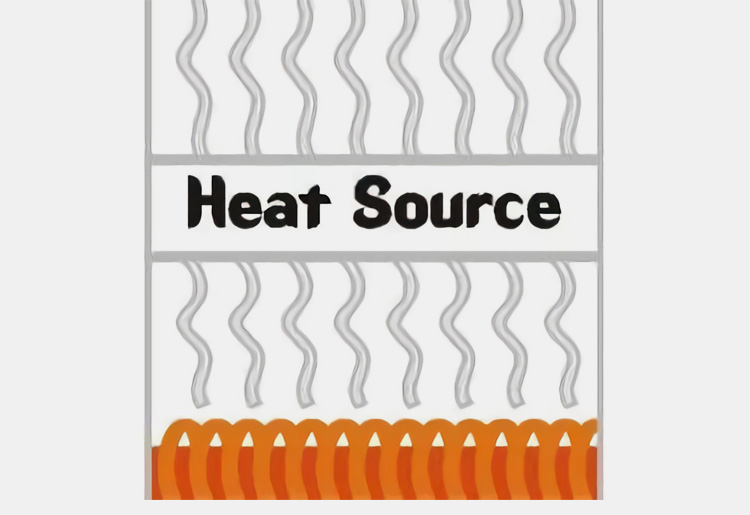
A heat source is necessary for heat shrink tunnels to create the heat that shrinks the film. This can come from infrared, hot air or steam heating. The heat source should be adequate to provide consistent temperatures across the entire tunnel chamber.
Cooling System
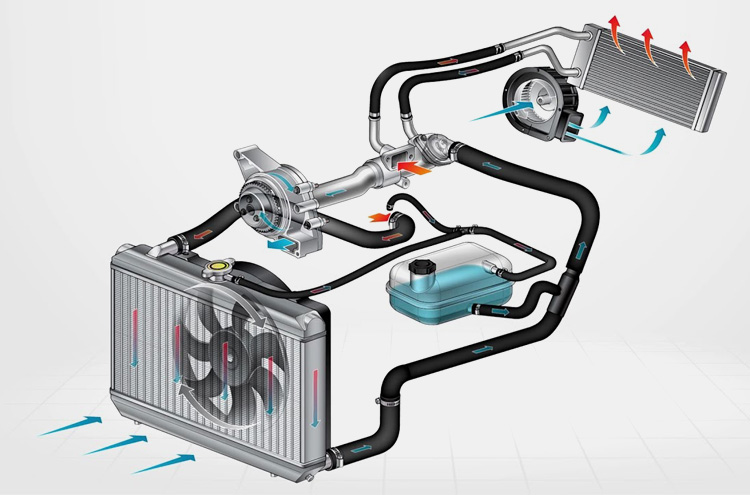
Once the heat-shrinkable film has been heated and shrunk, it needs to be cooled for its properties to be appropriately set. A cooling system is integrated into heat shrink tunnels to achieve this. Air or water cooling systems can be used depending on the application and the materials being processed.
Exhaust System
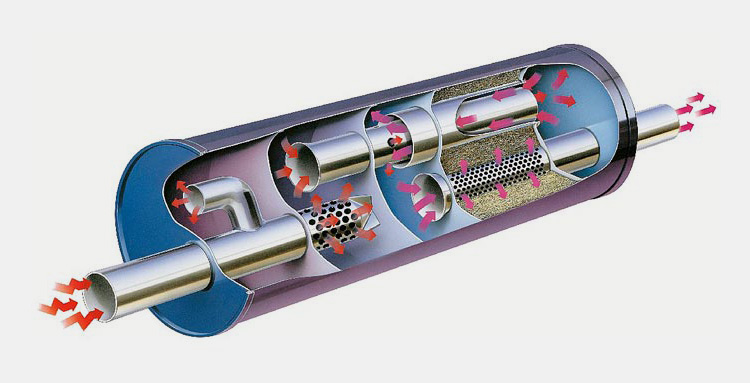
Heat shrink tunnels are typically equipped with an exhaust system that helps remove heat and humidity from the chamber after heat shrinking is completed and packages have passed through the heat tunnel. This helps maintain a safe working environment and reduces energy costs associated with heat shrink tunnels by removing excess heat from the chamber area.
Control Board

The control board is the part of the heat shrink tunnel that manages the heat source and conveyor belt speeds to heat and shrink films correctly and safely.
It may also be used to manage other features, such as exhaust systems, coolant systems and air flow rate, depending on the heat shrink tunnel used.
With an adjustable control board, heat shrink tunnels can be adjusted to process heat-shrinkable films of different sizes and thicknesses.
4.What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Operating A Heat Shrink Tunnel?
Wear Heat-Resistant Clothing And Safety Gear

It is important to wear heat-resistant clothing and safety gear when operating a heat shrink tunnel, as the heat generated in such an environment can be intense. This protective gear includes; heatproof gloves, long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and protective eyewear to protect from heat, steam, and flying debris.
Ensure Proper Ventilation
To ensure the area is safe to work in, adequate heat shrink tunnel ventilation must be maintained. Therefore, an exhaust fan or other suitable source of air movement is installed to keep air circulating and reduce heat build-up.
Stay Alert

As heat shrink tunnels are machines that generate heat and steam, it is crucial to stay alert while operating the tunnel. Also, you should be aware of any potential hazards and take proper measures to avoid them.
Use Caution When Handling Materials

When placing items into a heat shrink tunnel, use caution to ensure they are not stuck or blocked in the heating chamber. Also, be aware of heat build-up and possible burns on materials or hands.
Follow Maintenance Instructions

Regularly inspect heat shrink tunnels for any damage and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper cleaning, lubrication, and other necessary maintenance tasks to keep the machine running smoothly.
5.Which Materials Work Best In Heat Shrink Tunnels?
There are many materials that work well in heat shrink tunnels and can be used to produce a tight seal on products. These materials include:
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)

PVC is one of the most common materials in heat shrink tunnels, providing firm yet flexible finishing. It is heat resistant and produces a tight seal on products with uneven surfaces.
Polyolefin

This material offers excellent heat-shrinkage capabilities due to its low melting point. It is heat-resistant and produces a glossy finish.
Polyethylene

When applied, this strong, lightweight material has good heat-sealing abilities and excellent shrinkage characteristics. It also provides an airtight seal on products with uneven surfaces.
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)

PET is heat resistant and has excellent heat sealing characteristics. It produces a tight, glossy finish when heat is applied.
Polypropylene

This heat-resistant material can withstand high temperatures and has excellent shrinkage characteristics when applied heat. It produces a glossy finish that looks great on products with uneven surfaces.
Polystyrene

This heat-resistant material is great for heat-shrinking products with uneven surfaces due to its low melting point and excellent heat-sealing abilities. It also produces a glossy finish.
Aluminum Foil

Aluminum foil can be used in heat shrink tunnels because it offers good heat resistance, heat-shrinkage characteristics, and a glossy finish that looks attractive on products.
Glass
Glass can also be heat sealed with heat shrink tunnels due to its heat resistant properties, but it does not offer any heat-shrinkage characteristics. It is best used when a glossy finish is needed on the product and heat resistance is not an issue.
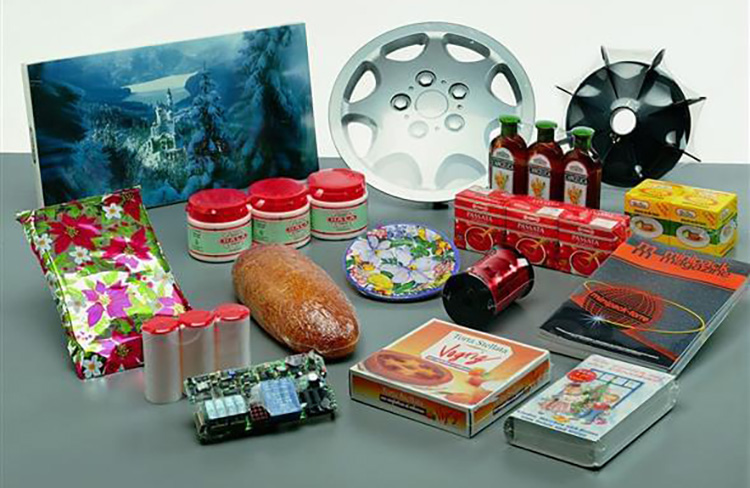
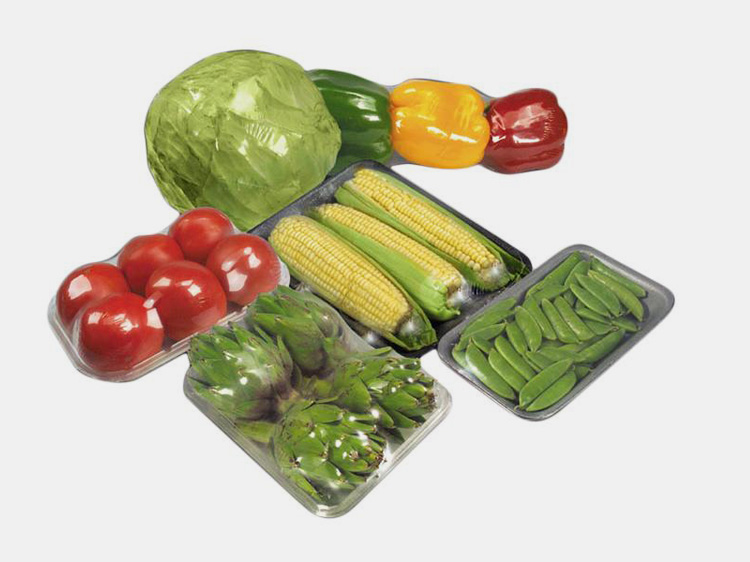
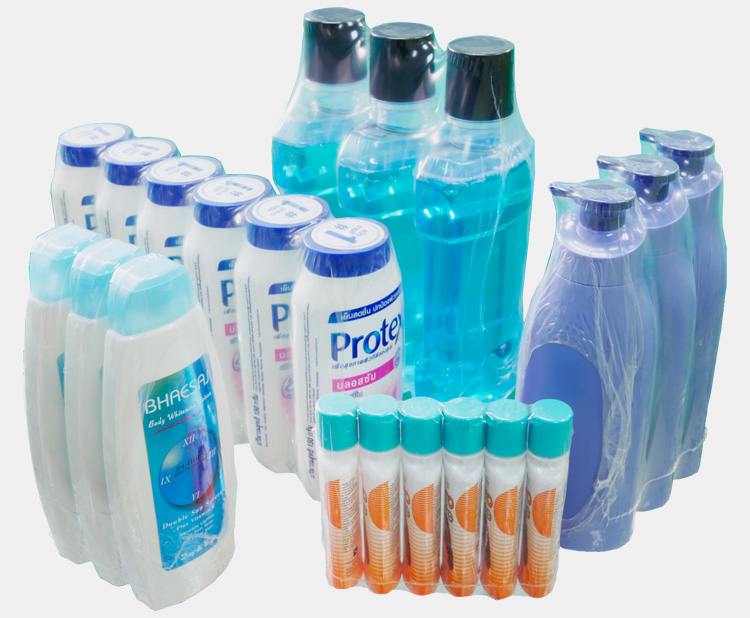
6.What Type Of Products Can Be Heat-Sealed and Packaged Using A Heat Shrink Tunnel?
Heat shrink tunnels can be used to package a variety of items, including:
Food Products

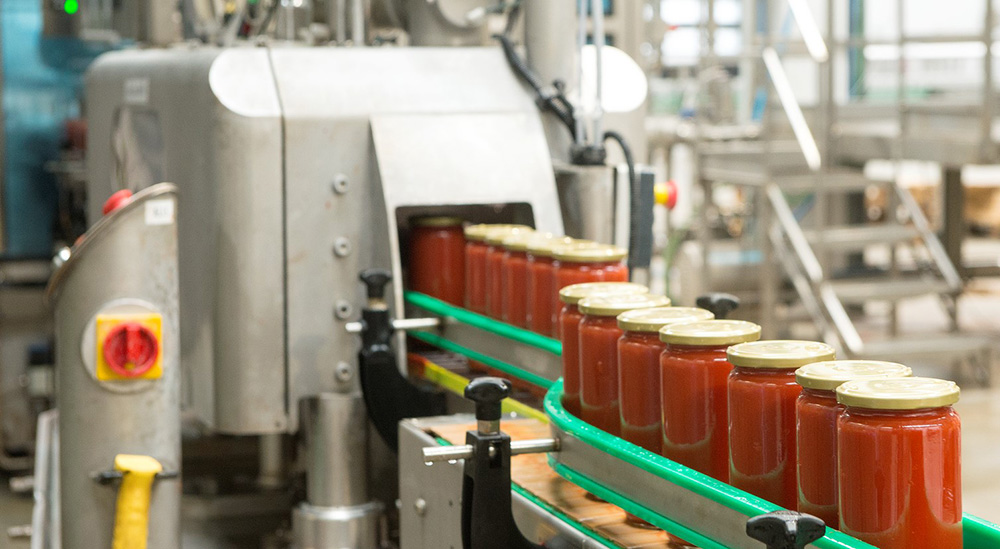
Heat shrink tunnels can package food products such as candy, snacks, cookies, crackers, biscuits, and other confectionery items. The heat sealing process seals the packaging, ensuring the product is protected from outside elements.
Electronic Items

Heat shrink tunnels are also used for packaging electronic components and products such as circuit boards, chips, transistors, and capacitors. The heat shrink tunnel ensures that these components are sealed securely within the packaging, protecting them from damage or contamination.
Chemicals and Liquids

Heat shrink tunnels can also package chemicals, solvents, liquid detergents, and other hazardous materials. The heat-sealing process ensures that these items are securely sealed within the packaging, safeguarding them from potential leakage or contamination.
Medical Equipment

Heat shrink tunnels are also used for packaging medical equipment such as syringes, needles, bandages, and other medical supplies. The heat sealing process ensures that these items are securely sealed in their packaging, protecting them during shipping and handling.
Books and Magazines

Heat shrink tunnels can also package books, magazines, and other paper products. The heat-sealing process ensures that these products are sealed securely within their packaging, protecting them during transportation and handling.
7.How Can Heat Shrink Tunnels Be Used To Improve Product Packaging Process?
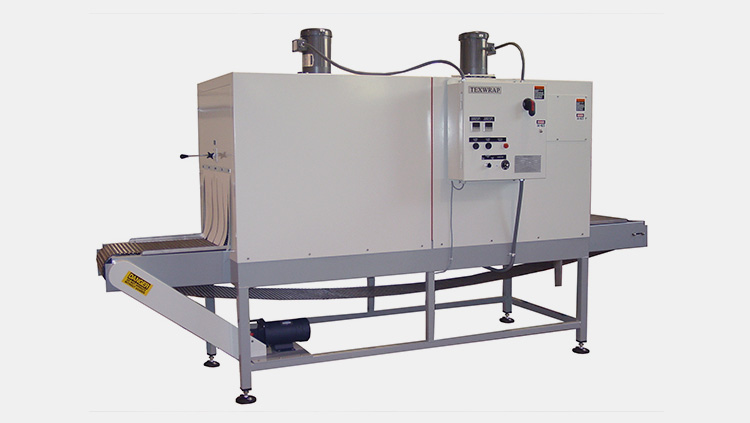

Increase Packaging Speed
Heat shrink tunnels can heat products quickly and evenly, allowing faster packaging speeds. The heat tunnel’s adjustable settings also allow you to customize the heat intensity to ensure that products are properly sealed.
Reduce Human Error
Using heat shrink tunnels reduces the chance of human error because a machine controls the temperature settings and timing of the heat application process. This ensures that each product gets consistent heat exposure, reducing the risk of under or over-heating, which can lead to faulty seals on packages.
Improved Product Quality

By ensuring that each product has been exposed to an equal amount of heat during the packaging process, shrink heat tunnels help maintain product quality standards across batches. This results in a consistent product quality that customers can trust.
Cost Savings

By reducing the amount of time and labor required for heat sealing, shrink heat tunnels can help reduce costs associated with packaging processes. The machine’s adjustable settings also allow companies to optimize heat levels to meet specific needs, further reducing energy costs.
8.What Factors Effect Heat Shrink Tunnel Speed?
The heat shrink tunnel speed can be affected by each of these factors,
Temperature
The heat shrink tunnel must be set at the correct temperature for heat-shrinkable materials to shrink effectively and adhere to product packaging. This, in turn, affects the speed of the heat shrink tunnel.
Product Size
Generally, more oversized products require a higher heat setting to ensure an evenly heat-shrunk surface. This means that the heat tunnel has to run slower to give enough heat energy to shrink any large products.
Shrink Film Being Used

Thicker heat-shrinkable films require more time in the heat-shrink tunnel to heat and shrink, which affects the heat-shrink tunnel speed.
Tunnel Length
The heat shrink tunnel length is essential for controlling heat shrink tunnel speed and heat transfer rate, as the longer heat shrink tunnel will require more time to heat products.
Airflow
High airflow is required for heat-shrinkable films to conform around products and packages properly. This heat shrink tunnel speed is affected by the size and power of the fans or blowers used.
Conveyor Speed

The conveyor speed is also vital for controlling heat shrink tunnel speed and must match the heat shrink tunnel heat rate for best results.
Operator Awareness
The operator’s awareness of the heat shrink tunnel operation is essential to ensure heat shrink tunnel speed is kept at optimal levels
Automation

Automated heat shrink tunnels are typically faster than manual heat shrink tunnels, as automated heaters can heat up in a shorter time.
9.What Are The Advantages Of A Heat Shrink Tunnel?

The heat shrink tunnel is a highly efficient and cost-effective packaging solution. Here are some of the benefits of using heat shrink tunnels:
Increased Productivity

Heat shrink tunnels enable higher production rates than manual hand wrapping, as they can automatically wrap multiple products quickly and consistently. This eliminates the need for additional labor costs, which results in increased productivity and reduced costs.
Versatility
Heat Shrink Tunnels are very versatile in packaging applications. They can be used for various sizes of products, and the heat-shrinking process can easily be adjusted to meet product-specific requirements.
Consistent Packaging Quality

With heat shrink tunnels, the finished product quality is consistent from one package to another. The heat generated during the process ensures that all packages have tight seals, eliminating any leakage or damage to goods inside the container.
Improved Safety Features
As heat is used during the heat-shrinking process, heat shrink tunnels have built-in safety features such as temperature sensors and heat-resistant plastic to protect workers from any heat-related injuries.
Speed and Efficiency

The heat tunnel provides a quick and efficient heat-shrink process, allowing for faster wrapping of products. This helps businesses to save time and money on production costs by increasing their output without compromising product quality.
Durability
The heat shrink tunnel helps to ensure that the heat-shrink packaging provides an optimal level of protection for the product ensuring its durability over time. This ensures that products can be safely transported and stored for extended periods.
10.What Are The Disadvantages Of A Heat Shrink Tunnel?

High purchase cost
Heat shrink tunnels are more expensive than other heat sealing devices because they require a considerable investment in heaters, blowers, and fans.
High energy consumption
Heat shrink tunnels require a lot of energy to heat up and operate, leading to higher electricity bills.
Space Requirements
Heat shrink tunnels are pretty large and occupy considerable space. This is problematic if you have limited floor space for your packaging operations.
Slow Production Speed
Using heat shrink tunnels can be slower than other heat sealing methods and require more time for product packaging operations. This can lead to reduced productivity and decreased efficiency in the entire process.
Heat Distribution Issues
Heat shrink tunnels may have heat distribution issues which can cause uneven heat throughout the tunnel, leading to inadequate heat sealing or improper shrinks of products that move through the tunnel. This leads to poor packaging results and wasted outcomes.
Maintenance Requirements

Heat shrink tunnels need regular maintenance to ensure proper operation and output quality. This can involve cleaning out fans, periodically changing heater elements, and checking wires, components, and other mechanisms.
Long Setup Times
It can take a significant amount of time to set up heat shrink tunnels for operation properly and requires an experienced operator or technician to make sure the equipment is correctly calibrated for optimal results. This adds extra overhead costs and can be pretty cumbersome.
Limited Versatility
Heat shrink tunnels are designed only for heat sealing and shrinking applications. They cannot be used for other packaging operations like heat sealing alone or laminating products with film or foil lids. This limits their use in some businesses where multiple processes must be done concurrently on the same production line.
Poor Quality Results

If heat shrink tunnels are not set up correctly, they can lead to poor heat sealing resulting in packages that cause customer dissatisfaction. Also, this procedure can have a negative impact on the brand image of a business.
11.What Are The Types Of A Heat Shrink Tunnel?
There are a variety of heat shrink tunnels available in the market. They include;
Infrared Heat Shrink Tunnel

These heat shrink tunnels use the heat generated by infrared radiators to heat and shrink the heat shrink film. This tunnel is often used in industries requiring precise heat and speed control, such as pharmaceuticals or electronics packaging.
Conduction Heat Shrink Tunnels

Conduction heat shrink tunnels are used for heat-shrinking thicker films since direct heat is applied more quickly and at higher temperatures. Also, direct heat allows for a more uniform heat distribution across the material being heat-shrunk.
Convection Heat Shrink Tunnels

Convection heat shrink tunnels are generally used for heat-shrinking applications that require less heat and faster speeds. The hot air inside the tunnel is evenly distributed, making it suitable for heat-shrinking of items of different shapes.
Steam Heat Shrink Tunnels
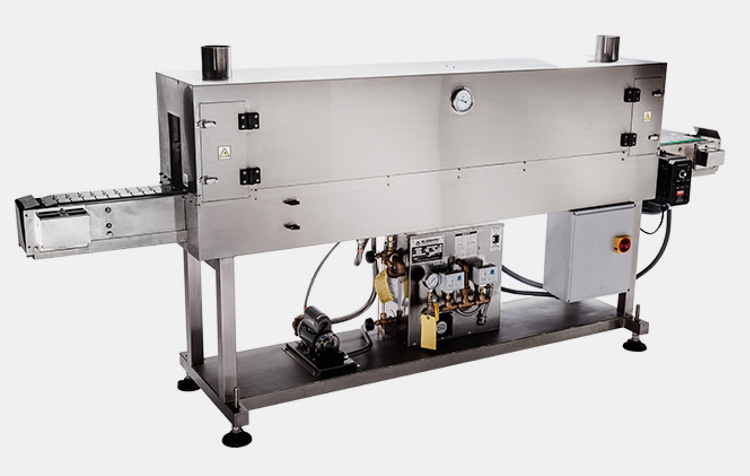

These heat shrink tunnels use steam heat to heat and shrink the shrink film. Steam heat provides a quick and even heat distribution, making it ideal for high-volume production applications.
Hot Air Heat Shrink Tunnels
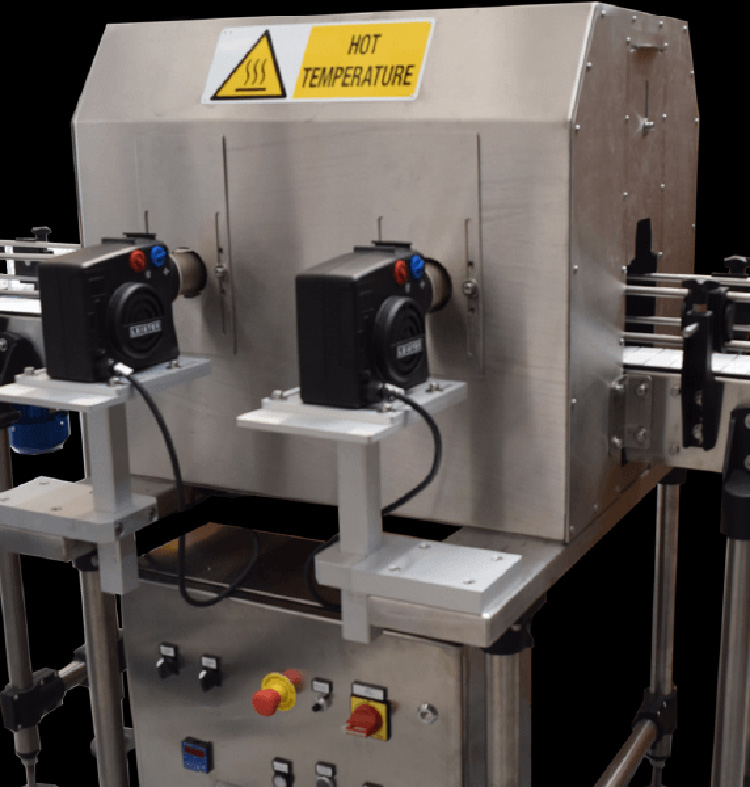

These heat shrink tunnels use hot air to heat and shrink the heat shrink film. This tunnel type is often used in applications requiring heat-sensitive products, such as heat-shrinkable labels or wire harnesses.
12.What Are The Applications Of A Heat Shrink Tunnel?
A heat shrink tunnel is an essential tool for a wide range of industries such as:
Food And Beverage Industry
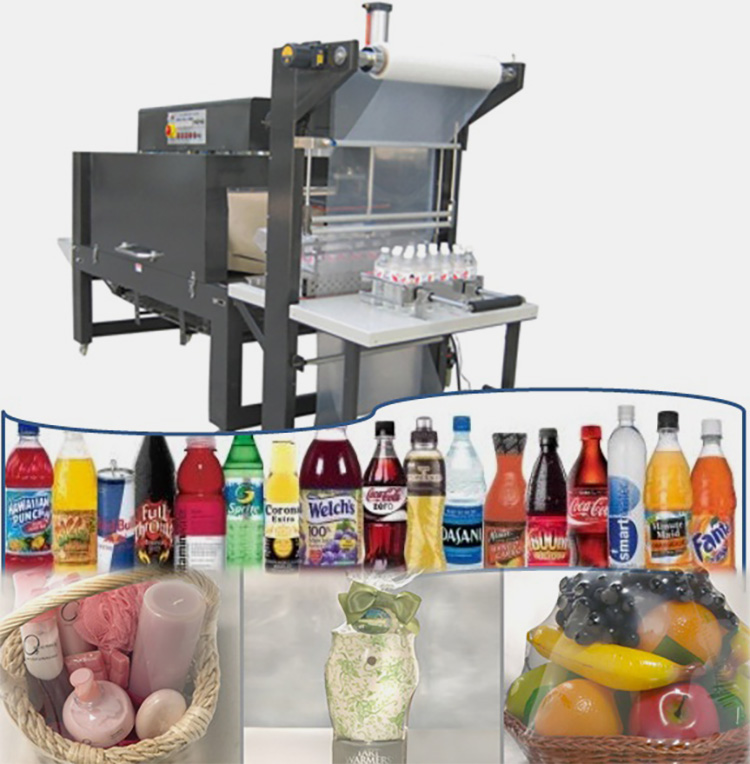

Heat Shrink Tunnels are used in food industry applications such as vacuuming, heat shrinking, bottle labeling, and overwrapping. This helps protect products while also making them visually appealing.
Retail Industry

Heat Shrink Tunnels help give product packaging a professional look, ensuring that goods arrive safely at their destination without any damage or tampering. It also enhances shelf appeal, thus drawing customers’ attention when shopping.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Heat Shrink Tunnels provide a secure, tamper-proof seal for medicine packaging. This helps to protect sensitive products while also maintaining their integrity throughout the entire supply chain process.
Printing Industry

Heat Shrink Tunnels can be used in printing applications such as heat-shrinking book covers or labels onto containers. This helps make the product look more attractive, thus increasing its marketability.
13.What Are The Common Problems Associated With Heat Shrink Tunnels?

Here are some of the most frequent problems associated with heat shrink tunnels:
Excessive Heat
Heat shrink tunnels require high temperatures to work and seal materials properly. However, excessive heat can cause heat damage to more heat-sensitive materials like plastic, which may cause them to break or melt.
Poor Air Circulation
Heat shrink tunnels require adequate air circulation to heat the material evenly. If there is insufficient airflow, some areas of the tunnel can become too hot or cold, leading to uneven heating and shrinkage or heat damage to the products.
Over-shrinking
If heat shrink tunnels are set too hot, they can over-shrink the material being packaged, leading to a tight fit that is difficult to open and may even tear or damage the product when opened.
Wrong size
Heat shrink tunnels can only heat materials within a certain size range. If the material is too large or small, it won’t heat properly and may not shrink evenly.
Wasted heat
Heat shrink tunnels generate heat that can escape into the environment if they are not properly insulated. This heat can be costly to replace and increase energy costs for businesses running heat shrink tunnels.
14.What Factors Determine The Shelf Life of Goods Packed By A Heat Shrink Tunnel?

The shelf life of goods packed by a heat shrink tunnel depends on various factors such as;
The Quality of the Heat Shrink Tunnel
Poorly maintained heat shrink tunnels can cause inconsistent heat application, reducing the shelf life of goods packed by them. Therefore, regular maintenance is essential for a heat shrink tunnel to deliver optimal performance.
Proper Packaging
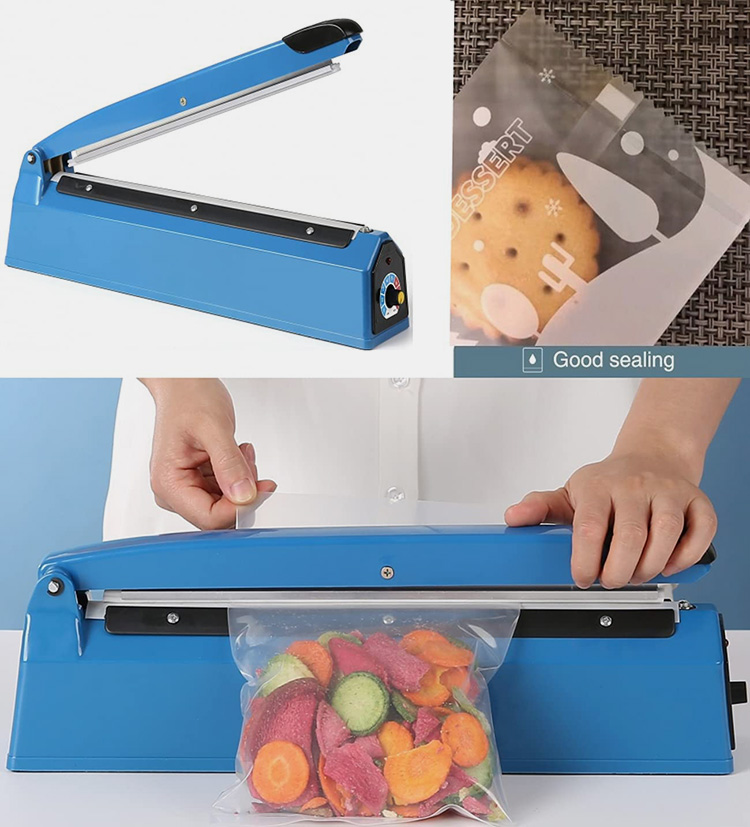

Taking time to package goods before heat sealing them can help preserve their shelf life by providing an additional layer of protection against dust, moisture, and other environmental elements.
Quality Control
Ensuring that heat shrink tunnels are regularly checked for temperature accuracy and proper operation is essential to ensure the maximum shelf life of heat-sealed goods.
Sealant Used

Different types of sealants have different lifespans, so choosing the right one for the job is crucial in determining the lifespan of products.
The Environment in Which the Goods Are Stored
Temperature and humidity can have a major impact on shelf life, so it is important to store goods in an area that is climate controlled as much as possible.
Proper Labelling of the Heat-Shrinked Package

This helps customers identify potential expiry dates or other information regarding the goods they purchase. It also helps to protect against counterfeiting and contamination.
15.What Safety And Environmental Concerns Should Be Taken Into Consideration When Using Heat Shrink Tunnel?
Temperature Control
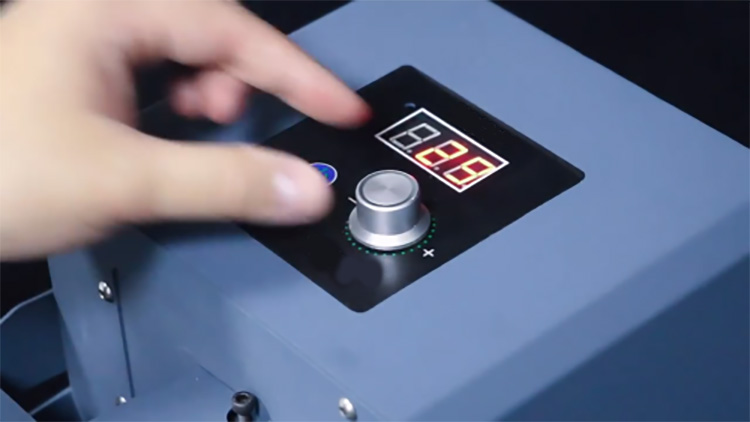

Heat shrink tunnels can reach extremely hot temperatures, so it’s essential that proper temperature controls are set up and monitored to ensure that users remain safe while using them.
Furthermore, these temperature controls should also be regularly maintained to keep heat levels consistent.
Air Quality
Poor air quality can cause health problems for those exposed to heat-shrink tunnels regularly, so it is important to ensure proper ventilation of the heat-shrink tunnel area at all times.
Moreover, heat shrink tunnels should be regularly cleaned to reduce dust or dirt build-up, which could contribute to poor air quality.
Fire Hazards
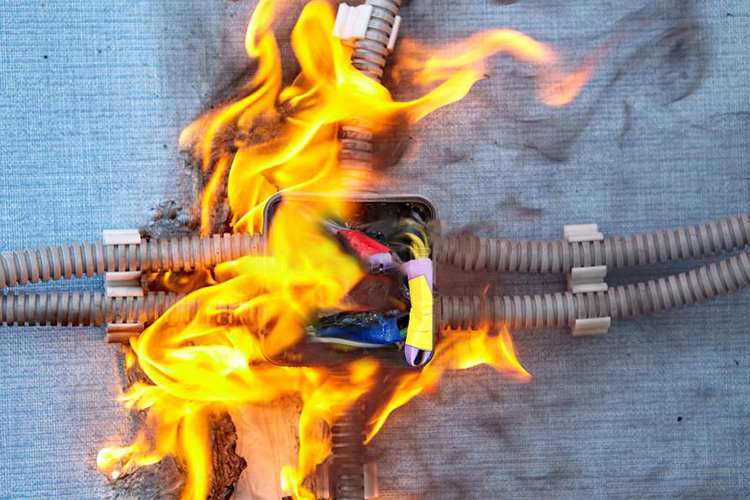

Heat shrink tunnels heat up and can cause a fire if the heat is too high or heat sources are not properly maintained. Therefore, it is important to ensure that heat shrink tunnels are regularly inspected and serviced to reduce the fire risk.
Emissions
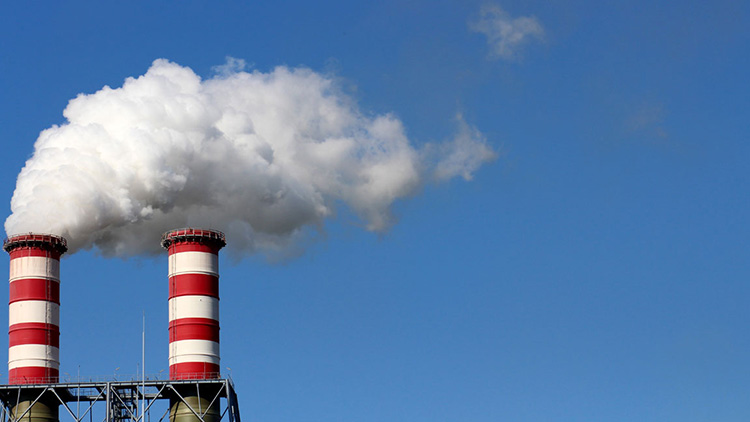

To prevent smoke and other potentially hazardous emissions from heat shrink tunnels, it is important to make sure they are well-ventilated by ensuring there is adequate air circulation around the machines at all times.
Chemicals and Gases
Heat shrink tunnels may emit potentially hazardous chemicals or gases, so users must be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate them. This includes wearing protective equipment when necessary and ensuring that all heat shrink tunnel components are regularly inspected and serviced.
16.What Factors Should Be Considered Before Purchasing A Heat Shrink Tunnel?
There are several factors that should be taken into consideration before purchasing a heat shrink tunnel
Size of Heat Shrink Tunnel

It is crucial to consider the size of the heat shrink tunnel you need before purchasing. The heat shrink tunnel should be sized according to the size and shape of your products.
Budget

Like any major purchase, your heat shrink tunnel should fit your budget. Consider the cost of the machine, as well as any installation costs or additional tools you may need to purchase or rent.
Features
Different heat tunnels come with additional features, so it is important to look for features such as adjustable speed conveyors, temperature control settings, and automatic shut-off mechanisms that will increase efficiency and reduce waste during operation.
Efficiency

Heat shrink tunnels are designed to quickly and efficiently heat-seal your products consistently. Therefore, you should ensure that the heat shrink tunnel you purchase has an efficient design that minimizes energy usage and allows for uniform heat distribution.
Maintenance

As with industrial machinery, heat shrink tunnels require regular maintenance and upkeep to keep them ideal during operation.
Temperature Levels
It is important to select a heat shrink tunnel that can provide the heat level needed for your products. The temperature range of heat shrink tunnels varies widely depending on the heat source, so be sure to research what level of heat your tunnel can produce before purchasing.
Safety
Another factor to consider when purchasing heat shrink tunnel is the safety features it offers. The heat source of the heat shrink tunnel should be enclosed in a sealed chamber which ensures that employees are not exposed to direct heat, and all components of the heat shrink tunnel should be built to safety standards.
Ease to Operate

It is important to select a user-friendly heat shrink tunnel with a simple user interface. Ease of use will ensure that your heat shrink tunnel is used safely and efficiently.
Conclusion
A heat shrink tunnel is a versatile and easy to operate machine that can be used for a number of applications. Also, this tunnel features an infrared heating system that evenly distributes heat throughout the chamber, ensuring all products are properly shrunk. Therefore, if you are looking for a reliable and high quality heat shrink tunnel, contact Allpack. Our team of experts will help you find the perfect heat shrink tunnel for your needs.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide

Heat Shrink Tunnel:The complete FAQ Guide in 2024 Read More »