Vacuum Feeder: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2024

Do you have trouble with your cats constantly begging for food or making a mess when they eat? Are you interested in finding an easier way to feed them without having to strain yourself? Then the vacuum feeder might be your answer!
This innovative pet product has taken feeding animals to the next level and helps make caring for pets much more convenient. With its easy-to-use design, no mess functions, and healthy nutritional benefits, it’s perfect for busy pet owners who want their furry friends well looked after while keeping their home clean.
In this blog post, we will outline how vacuum feeders work, their features, and why they’re becoming more popular among pet owners who want an easier feeding routine.
1.What Is A Vacuum Feeder?
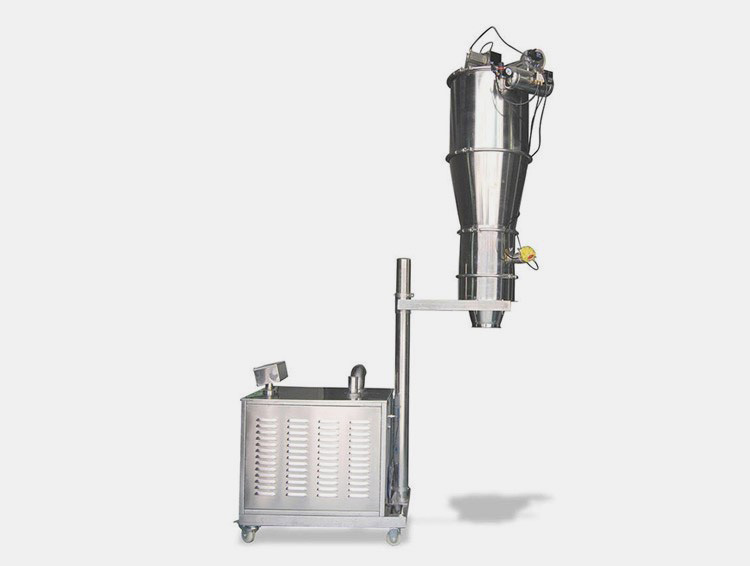

A vacuum feeder is an automated device that moves powdered, granular, and liquid materials from a source to a destination. It involves using vacuum suction to draw material from one location, such as a bin or hopper, and transfer it through tubes for discharge into another container.
Vacuum feeders are used in many production processes where accuracy and repeatability are important. They provide precise control over the flow rate, allowing for extremely accurate material dispensing.
Also, this equipment can transport large volumes of material quickly and efficiently without manual labour, making them cost-effective solutions in many industrial applications. Vacuum feeders offer flexible design options depending on the application requirements, including configurations with open hoppers or enclosed bins connected via vacuum lines.
Moreover, these vacuum feeders can also be used with other equipment, such as mixers, blenders, and particle size reduction machines, to ensure the precise mixing or grinding of particles. Vacuum feeders are widely used in many industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, chemicals, plastics, etc.
2.What Are The Components Of A Vacuum Feeder?
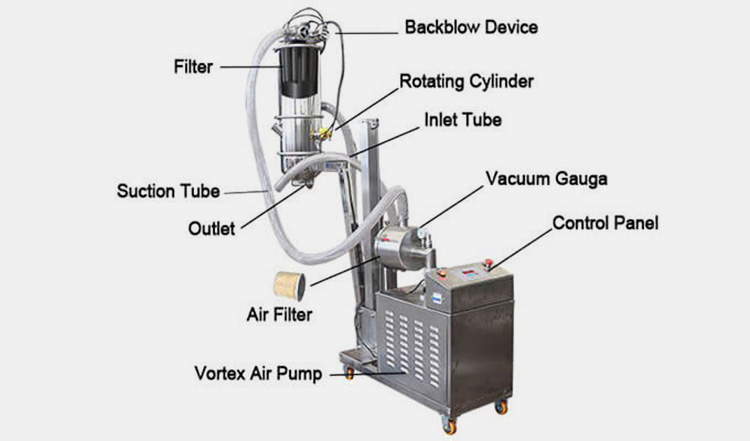

A vacuum feeder consists of several components, including:
- Vacuum Pump
This is the primary component of a vacuum feeder and creates an area of low pressure to draw material into the feeder.
- Air Regulator
This component regulates the pressure within the vacuum system, ensuring that it remains at the optimum level for efficient material flow.
- Vacuum Chamber
This is where the vacuum pressure is created and maintains the vacuum feeder system. It also collects excess material that the vacuum cannot draw in.
- Adjustable Speed Motor
The adjustable speed motor controls how quickly material is fed into the feeder, allowing for precise control of the material flow.
- Exhaust Tube
The exhaust tube is necessary to ensure that no excess vacuum pressure builds up in the vacuum chamber, as this can cause damage to the vacuum feeder system.
- Hopper
This is used to store material before being sucked into the vacuum feeder. The size and shape of the hopper will depend on the type of vacuum feeder system used.
- Control Panel
This is used to monitor, adjust and control all aspects of the vacuum feeder system. It also allows for troubleshooting should any issues arise.
3.What Are The Advantages Of A Vacuum Feeder?
A vacuum feeder has a wide range of advantages to offer, including:
- Cost Savings

Vacuum feeders reduce the need for manual labour and increase the consistency of product output while using minimal energy, resulting in cost savings. This makes vacuum feeders an excellent investment for material handling processes.
- Reduced Product Damage
Vacuum feeders help reduce product damage in the feeding process. This is because vacuum suction reduces mechanical shock and air that can cause product breakage or separation, resulting in a more uniform output.
- Increased Accuracy
The vacuum feeder controls the rate of material flow into a process based on vacuum pressure, as opposed to manual operation or vibration, which may result in inconsistent feed rates. This makes vacuum feeders ideal for ensuring accurate product delivery and more consistent results.
- Improved Safety
Vacuum feeders are safer than traditional material handling methods because they reduce the need for operator interaction with dangerous materials while also reducing dust and other airborne particles.
- Space Saving
Vacuum feeders are designed to be compact and take up less space than other material handling equipment, making them ideal for tight areas or processes with limited floor space.
4.What Are The Applications Of A Vacuum Feeder?
- Pharmaceutical Industries

Vacuum feeders are used in pharmaceutical industries to convey and disperse powder, granules and pellets.
- Food Manufacturing

Vacuum feeders are commonly used to transport grains, nuts, dried fruits, powders, etc. as raw materials for food processing.
- Cosmetics Manufacturing
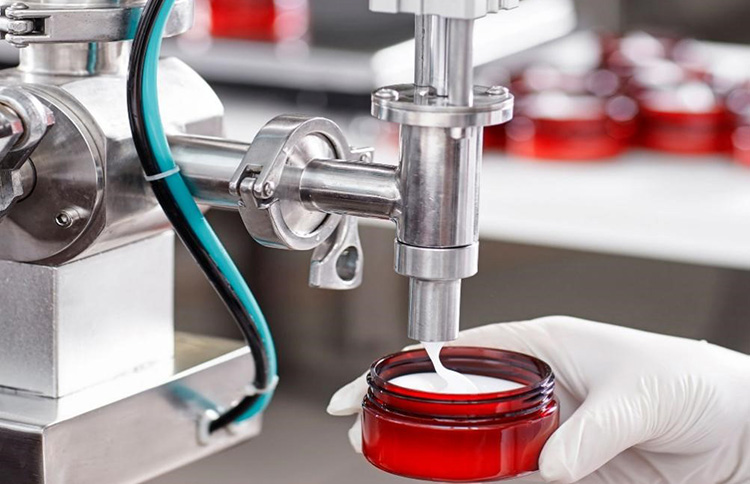

Vacuum feeders are used in cosmetics manufacturing to add ingredients such as colorants and fragrances into the mixers.
- Chemical Industries

Vacuum feeders can be used in chemical industries to convey and disperse powder, granules and pellets.
5.How Does A Vacuum Feeder Work?
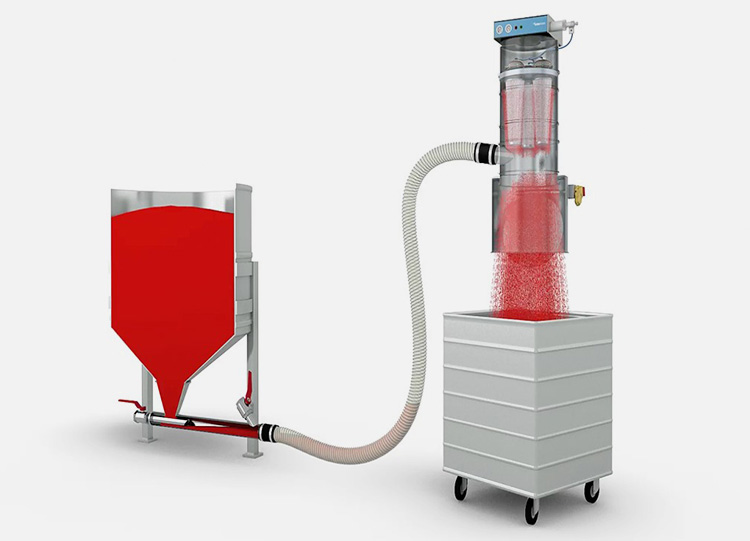

A vacuum feeder works by using vacuum suction to pick up the material and deposit it into a container. The vacuum feeder creates a vacuum in its chamber, which creates an air flow that pulls in the material and deposits it into containers or vessels on the other side.
6.What Are The Different Types Of Vacuum Feeders Available For Industrial Applications?
a) Automatic Vacuum Feeders
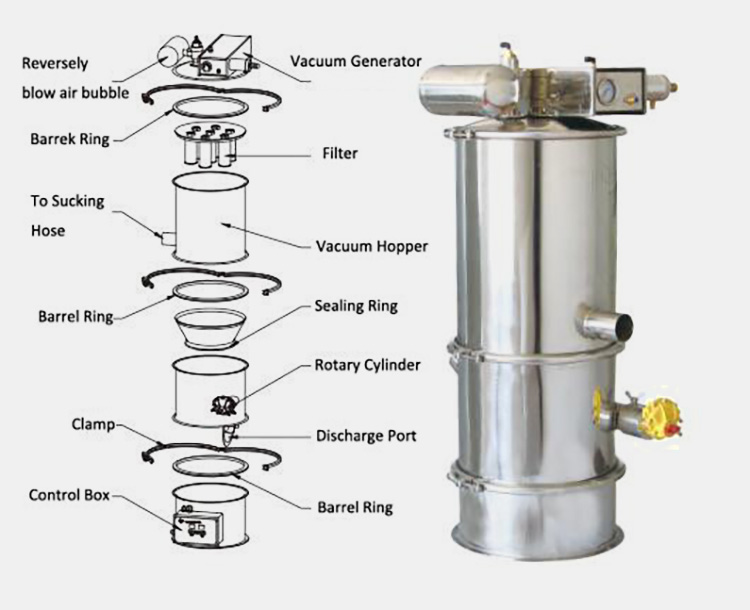
Automatic vacuum feeders are automatic pet feeders that use suction technology to precisely dispense small portions of food and treats. They are designed to give pets a comfortable and consistent meal experience with minimal mess. These feeders feature adjustable settings so you can customize the amount of food or treat each time, ensuring your pet receives the proper portion size every time.
Components
- Vacuum Pump
The vacuum pump is the heart of an automatic vacuum feeder, and its main function is to generate a vacuum in order to draw material from the hopper into the machine. It can either be air-powered or electric-powered depending on your needs.
- Hopper
The hopper is the container where the material to be fed is stored. It must be large enough to hold the necessary amount of material and should also be designed in such a way that it allows easy access for maintenance purposes.
- Feeding Mechanism
This is usually a conveyor belt or auger, which transports the material from the hopper into the machine. It is important that the feeding mechanism is able to handle the material properly, as this will affect the performance of the automatic vacuum feeder.
- Control System
The control system is responsible for controlling how much material is drawn into the automatic vacuum feeder at any given time. It can be controlled manually or automated with a microprocessor.
- Dewatering System
This is an optional component that can be used if your automatic vacuum feeder needs to process wet material. It consists of a dewatering unit, which separates the water from the material, and then recycles it back into the hopper for further processing.
- Discharge Chute
The discharge chute is where the material exits the automatic vacuum feeder. It must be designed properly in order to ensure that it does not clog, and that the material is discharged evenly into its designated area.
- Sensors
Sensors are a key component of automatic vacuum feeders as they help to monitor the performance of the machine and detect any potential issues early on. Some common sensors used in automatic vacuum feeders include pressure sensors, level sensors, and temperature sensors.
Working Principle
Automatic vacuum feeders use a combination of suction and pressure to move items from one location to another. They work by creating a vacuum inside the feeder, which draws air in and creates negative pressure. This vacuum then pulls the items through the feeder for automatic sorting, counting, and positioning
Applications
Automatic vacuum feeders can be used in a wide range of applications from industrial manufacturing to everyday household tasks. In industrial settings, automatic vacuum feeders are often used for automatic material handling and robotic assembly lines.
In the home setting, automatic vacuum feeders are most commonly used for pet food/water bowls, automatic litter boxes, automatic pet doors, fish tanks and aquariums
b) Belt Vacuum Feeders

Belt vacuum feeders are used for transporting small parts from one area to another. The belts provide a continuous, smooth motion which helps to ensure that the parts are transported safely and efficiently.
Components
- Vacuum Belt
The belt is a conveyor belt with holes throughout it that suck in material and transport it along the belt. It can be made of various materials such as rubber or polyurethane, and is driven by an electric motor.
- Vacuum Generator
This component creates the vacuum that powers the belt. It is usually a fan or pump driven by an electric motor.
- Hopper
The hopper is used to store material before it’s transferred onto the belt. It can be made of various materials such as metal or plastic and is designed to hold a certain amount of material.
- Control System
This component is responsible for controlling the speed, pressure, and direction of the belt vacuum feeder. It can be either manual or automated and consists of motors, sensors, switches, and other electronics.
- Conveyor Chute
This component is a channel that directs the material from the belt feeder to its destination. It can be made of various materials such as metal or plastic and is designed to ensure that the material does not get stuck in any spot along the belt.
- Support Structure
This component provides structural support for all of the other components and ensures that the belt vacuum feeder remains in place. It is usually made of metal and can be either free-standing or mounted to a wall.
Working Principles
The belt vacuum feeder works by creating a negative pressure within the system, allowing materials to be drawn up onto the belt and transported along the belt run. This allows for efficient and continuous movement of bulk materials with minimal dust or material loss.
The belt vacuum feeder is comprised of a belt, belt drive mechanism, and an adjustable suction hood with a vacuum source. The belt runs between two sprockets driven by the belt drive mechanism which creates continuous movement along the belt run.
A suction hood is placed over the belt and connected to a vacuum source, creating a negative pressure or suction which pulls the material onto the belt. The belt is then able to transport the bulk material to its desired location.
Applications
Belt vacuum feeders are used in a variety of industries, such as mining, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. In mining applications belt vacuum feeders can be used to transport bulk materials from underground deposits to the surface quickly and efficiently.
In food processing belt vacuum feeders can be used to transport grain and other food products from silos to storage facilities.
c) Linear Vacuum Feeders
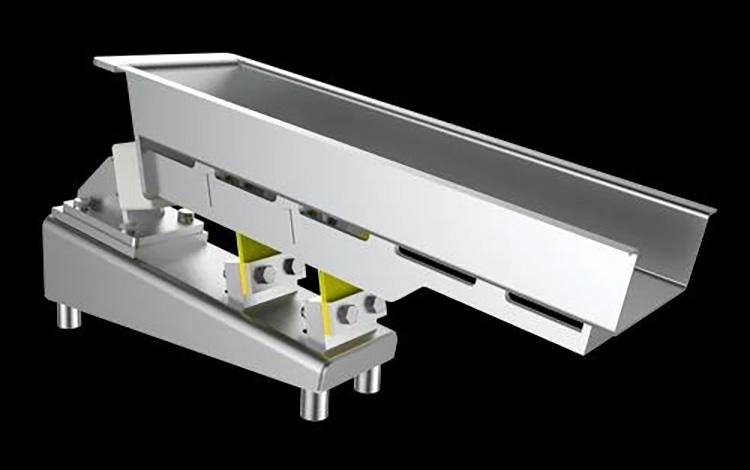

Linear vacuum feeders are automated systems used to transport and dispense particulate materials. They feature linear, motor-driven hoppers that work in tandem with a powerful vacuum system to quickly and accurately distribute dry bulk ingredients. This type of equipment is commonly used in food processing, chemical production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and other industries.
Components
- Vacuum Generator
A linear vacuum feeder consists of a vacuum generation section, which is mostly powered by an electric motor and/or compressed air. This generates the necessary suction to move material along the linear feed path.
- Linear Pathway
The linear pathway consists of tubing or other flexible conduit that carries the material from the vacuum generator to its desired location. The linear path must be properly designed to provide a tight fit and make sure that no vacuum leaks or other obstructions occur.
- Vacuum Sensor
A linear vacuum feeder also comes equipped with a vacuum sensor, which is used to monitor pressure changes in the linear pathway. This helps maintain consistent flow rates and allows the linear vacuum feeder to operate at optimal performance levels.
- Control Unit
The linear vacuum feeder is controlled by a control unit, which is responsible for regulating the speed and power of the linear path. It also monitors the pressure changes in order to ensure that material is being moved at the desired rate.
- Safety Devices
Linear vacuum feeders also come equipped with safety devices such as emergency stop switches, overload sensors and limit switches to help protect personnel and equipment from potential damage during operation.
- Material Container
Finally, linear vacuum feeders include a material container which is used to store the material that is transported along the linear path. This container must be properly sized to ensure proper flow and prevent clogging of the linear pathway.
Working Principles
Linear vacuum feeders work by creating a negative pressure or vacuum within the linear tube, which causes air pressure to push material along through the linear tube.
The linear tube also typically contains a series of baffles and other components that help ensure that the material is moving steadily and evenly.
By controlling the speed at which materials move through the linear tube, linear vacuum feeders can be used to handle a wide variety of products, including both light and heavy materials.
Applications
Linear vacuum feeders are used in a variety of industrial, medical, and commercial applications. In industrial settings, linear vacuum feeders can be utilized to transport items such as powders and pellets over long distances or up steep inclines.
Linear vacuum feeders are also commonly used to segmentally process products such as potato chips or snacks. In medical applications, linear vacuum feeders may be used to transport pharmaceuticals and medical supplies or to package pre-filled syringes.
Additionally, linear vacuum feeders are frequently utilized in commercial settings for lightweight and low cost product packaging solutions.
7.What Are The Different Types Of Materials That Can Be Handled By A Vacuum Feeder?
The types of materials that a vacuum feeder can handle include:
- Granular Materials

These are materials such as: sand, sawdust, coffee grounds, and sugar. The vacuum feeder can easily move these materials from one place to another without causing damage or spillage.
- Powdered Materials

These are materials such as flour, baking powder, and spices. The vacuum feeder can collect and store these materials in a dust-free environment.
- Pellets

These are small cylindrical or spherical shapes made from materials such as plastic or wood. A vacuum feeder can handle these pellets without causing any damage to them.
- Tablets and Capsules
These are solid circular discs that contain medicine or other ingredients. The vacuum feeder can easily transfer these tablets and capsules from one point to another while keeping them contained within the vacuum chamber.
8.How Can You Design Vacuum Feeders For Optimal Performance?
Regarding vacuum feeders, proper design is key to achieving optimal performance. To ensure maximum performance, the vacuum feeder must be designed with certain considerations. They include:
- Material Selection
What type of material will the vacuum feeder be working with? Different materials require different types of vacuum systems. They may need special modifications, such as adding side shields or replacing the suction cups with larger ones that can handle heavier loads.
- Vacuum System
The type of vacuum system used should also be considered; vacuum systems with lower airflows may not be able to handle heavy loads, while higher airflows can create too much suction, leading to damage or malfunction.
- Size and Shape
The vacuum feeder’s size and shape must also be considered when designing for optimal performance. The vacuum system must fit properly in the available space so it can move freely and efficiently without obstructions.
If the vacuum feeder is too small, then it won’t be able to provide enough suction for heavier materials; if it’s too large, then it will take up unnecessary space and cause difficulties in maneuvering.
- Safety
Finally, the vacuum feeder must be designed with safety in mind. All moving parts of a vacuum feeder should be properly guarded, and any areas that could pinch or crush material must be blocked off.
Additionally, vacuum systems should be equipped with sensors to detect objects or materials in the vacuum feeder’s path so that action can be taken before an accident occurs.
9.What Are The Maintenance Procedures For A Vacuum Feeder?
- Inspection

Inspect the vacuum feeder to ensure there are no blockages or clogged lines that could disrupt vacuum flow and material handling processes.
- Cleaning
Vacuum feeders should be cleaned regularly to ensure optimal performance and prevent dust accumulation from compromising the vacuum flow. Be sure to clean any filters, hoses, valves, and other parts of the vacuum feeder system as needed.
- Testing

The vacuum level must be tested regularly to maintain efficient material handling operations. A vacuum tester can help you determine what type of pump is most suitable for your application and if it is operating at a sufficient vacuum level.
- Adjust vacuum settings
If the vacuum levels are not at the desired setting, you may need to adjust the vacuum pressure accordingly. This can help optimize material handling performance and ensure that your vacuum feeder operates at peak efficiency.
- Lubrication

Vacuum feeders require regular lubrication of moving parts like bearings and valves to reduce friction and wear-and-tear on the vacuum feeder system. Be sure to use a vacuum-safe lubricant when servicing vacuum feeders.
10.What Safety Measures Should Be Taken When Using A Vacuum Feeder?
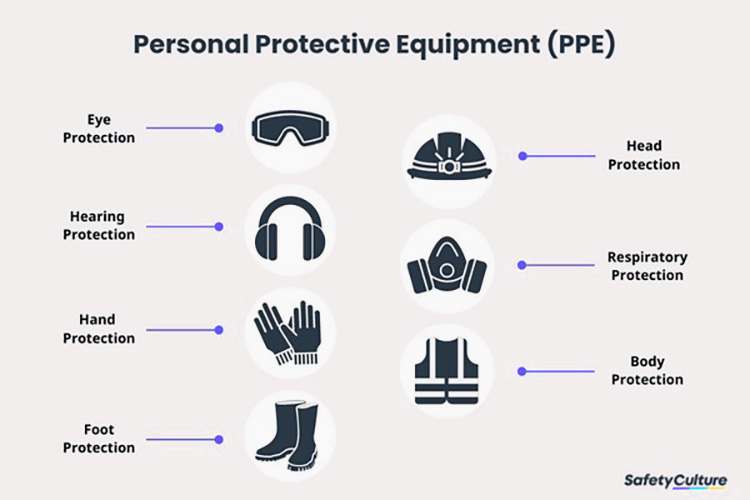
- Wear Protective Clothing
When operating vacuum feeders, it is essential to wear safety glasses and hearing protection. Long-sleeved shirts and pants should also be worn to protect skin from any flying debris or sparks that may occur during the operation of a vacuum feeder.
- Read The Manual
Always read the vacuum feeder’s operator manual before using it. This will ensure that you thoroughly understand the vacuum feeder’s operation and all safety requirements.
- Keep Your Workplace Clean.
Ensure that your vacuum feeders are cleared of debris, dust, and dirt before operating them. Doing so can help prevent fires or electrical hazards from occurring.
- Use Vacuum Feeders With Caution
Operate vacuum feeders slowly and carefully. Ensure that all hoses are secure before operating the vacuum feeder, and keep your hands away from moving parts while in operation.
Also, make sure to turn vacuum feeders off when not in use and unplug them before changing or cleaning the vacuum feeder.
- Maintain Vacuum Feeders Properly
Regularly inspect your vacuum feeders for any signs of damage, including worn components and loose wires. Replace damaged parts immediately, and follow the maintenance instructions outlined in the vacuum feeder’s manual.
- Training Operators
Ensure that all vacuum feeder operators are trained and certified before using a vacuum feeder to ensure they know how to use it safely and effectively. This will also help to reduce any risk of misuse or accidents.
11.What Are The Common Faults Associated With Using A Vacuum Feeder And Their Possible Solutions?
- Clogging

When particles become stuck in the vacuum lines, it can cause clogging, which prevents material from flowing through properly.
Solution
To fix this problem, anti-clogging filters should be installed at strategic points along vacuum lines to prevent particles from entering the vacuum chamber and causing blockages.
- Inefficient Flow Rate
If there is an insufficient flow rate of materials being fed into the vacuum feeder, then this can cause problems and inefficiencies.
Solutions
Replacing the seals or tightening vacuum control valves, ensuring that no air is allowed to enter the chamber and thereby creating a vacuum in the system.
- Leakage

Vacuum feeders can suffer from leakage due to worn seals or vacuum loss within the system.
Solutions
Adjusting vacuum levels, checking the system for air leaks, and ensuring that all vacuum lines are connected properly.
- Malfunctioning Vacuum Sensors
If vacuum sensors are malfunctioning or not operating correctly, this can lead to inconsistent vacuum levels and inefficient material flow.
Solutions
Replace any faulty vacuum sensors or adjust their settings. Additionally, regular maintenance should be done on the vacuum feeder to ensure everything is functioning properly.
- Contamination
Contamination from foreign materials can also disrupt the efficiency of vacuum feeders.
Solution
Use a filtration system designed to filter out any contaminants before entering the vacuum system.
Additionally, it is important to regularly clean vacuum lines and chambers to keep them free of debris or other materials that could cause blockages.
12.What Factors Should Be Taken Into Consideration Before Purchasing A Vacuum Feeder?
- Cost

The cost of a vacuum feeder will depend on its size and features, so it is important to consider your budget before making a purchase.
- Size
Vacuum feeders come in different sizes, so you’ll need to decide which one can accommodate the size of your operation.
- Durability
Make sure that the vacuum feeder you’re considering is made from materials that can withstand wear and tear over time.
- Maintenance

Consider how often the vacuum feeder needs to be serviced and maintained, as this can have an impact on the cost of ownership over time.
- Efficiency
Determine if the vacuum feeder has features that improve efficiency, such as sensors or a built-in timer.
- Warranty
Check to make sure that the vacuum feeder comes with a warranty so that any problems can be addressed quickly and effectively in the future.
Conclusion
With a wide range of options for sizes, shapes, colors, and features; the chances are good that Allpack has the perfect vacuum feeder for your business. If you have any questions or would like more information about our products and services, please don’t hesitate to contact us today. Our team is always ready and willing to help you find exactly what you need to take your business to the next level.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
The Buyer's Guide

Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours